What is the ERP system?
ERP stands for Enterprise Resource Planning, loosely translated as Enterprise Resource Planning System. That's the linguistic interpretation, so what is the true essence of ERP?
The pharmaceutical sector increasingly emphasizes the maintenance of safety and quality in production, especially concerning data management through software systems. Assessing software compliance with Good Manufacturing Practices according to European standards (EU-GMP) is not only crucial but also an essential step to ensure that businesses in the industry adhere to the highest regulations and standards regarding safety and quality. This article addresses common questions about evaluating ERP software according to EU-GMP standards and explores the benefits of using PharmaSoft ERP software to enhance compliance and efficiency.

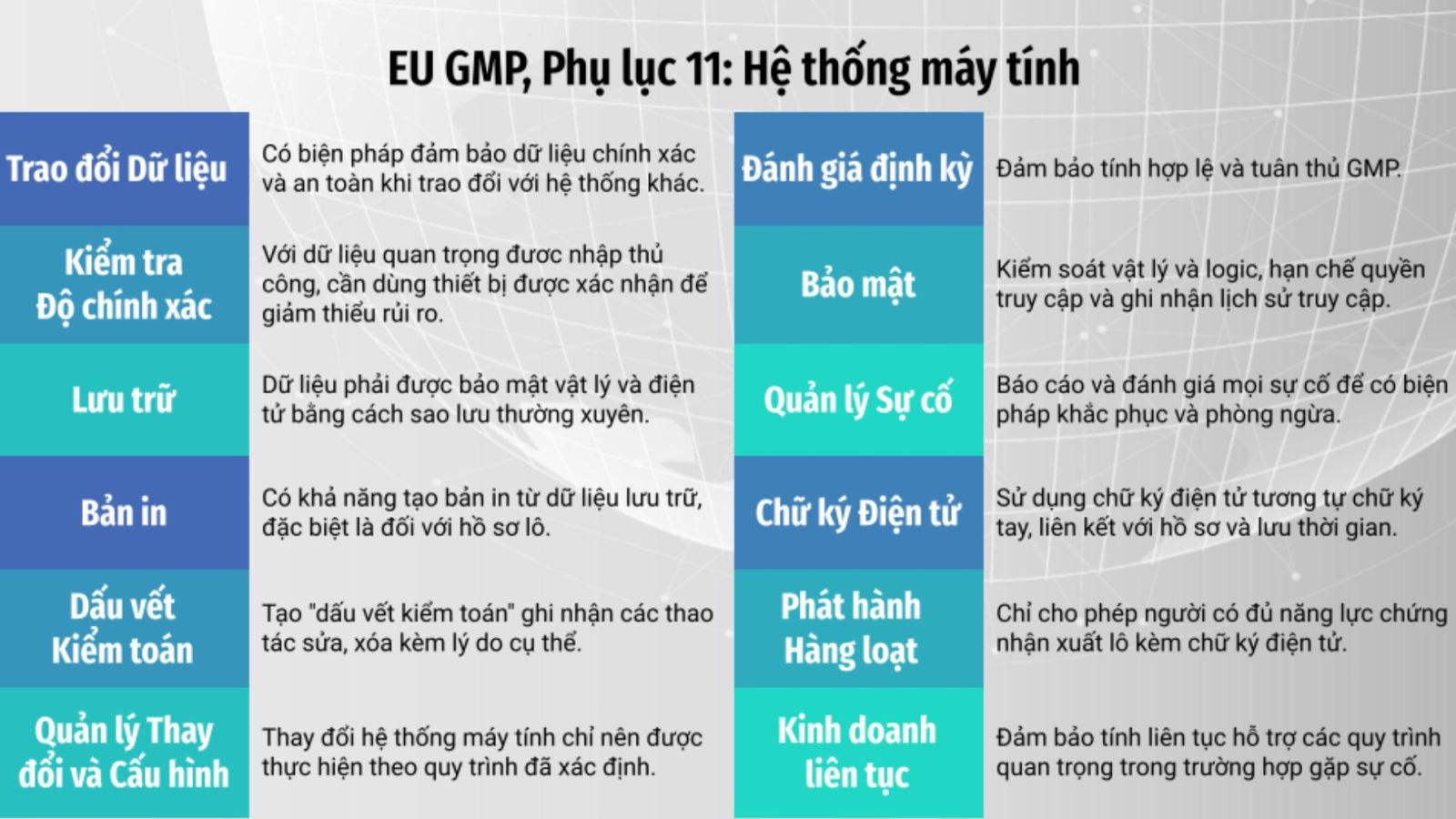
One of the crucial factors in meeting EU-GMP standards is the implementation of Computerized System Validation (CSV). Computerized systems used in activities related to the production, quality control, and distribution of pharmaceutical products must comply with the requirements of Annex 11, EU-GMP. These requirements aim to ensure that computerized systems are reliable, consistent, and highly integral, as well as capable of preventing, detecting, and handling errors and misuse.
Validation is assessing and providing evidence that a computerized system or one of its components meets predefined requirements and operates as expected.
A typical example of a system that needs validation is ERP software. ERP stands for Enterprise Resource Planning, a business management software system that helps organize business activities such as finance, human resources, manufacturing, sales, customer relationship management, and supply chain. ERP can improve efficiency, reduce costs, and increase profits for pharmaceutical manufacturing enterprises. However, ERP can also risk quality, safety, and legal compliance if not thoroughly validated and controlled.
Therefore, pharmaceutical manufacturing enterprises must adhere to GMP standards, especially Annex 11 of EU-GMP, when using computerized systems, including ERP software solutions. This ensures that computerized systems can effectively and safely support the production, quality control, and distribution of pharmaceutical products.
The validation of ERP software plays an extremely important role in the implementation of enterprise systems. Validation ensures that the developed software meets specific requirements and accurately describes the system's functions. Through the validation process, the functions of ERP software are meticulously examined to ensure completeness and accuracy, from resource management to the automation of business operations. This helps create an efficiently operating ERP system, tailored to the specific needs of the organization, providing long-term value to the business.
ERP software validation is not only a technical process but also a tool to maintain data integrity according to the principles outlined in GMP standards. This ensures that data generated, processed, and stored in the ERP system is accurate, traceable, and most importantly, not tampered with. This helps protect the reliability of crucial information in pharmaceutical manufacturing.
Moreover, ERP software validation plays a crucial role in complying with EU-GMP standards, especially in the context of Annex 11. Emphasizing the importance of ensuring secure and controlled access to computerized systems, plays a vital role in preventing unauthorized access and keeping data secure.
ERP software validation not only enhances the transparency of the process but also limits user access rights. This measure not only reduces the risk of unauthorized modifications but also ensures that every action in the system can be traced and accounted for by specific individuals, meeting the stringent requirements of GMP.
The stringent regulations mentioned above, combined with the support of ERP PharmaSoft, not only assist pharmaceutical businesses in complying with EU-GMP regulations but also optimize the performance of the ERP system, ensuring data integrity in the manufacturing environment. In the next section, we will address key questions related to the validation process of ERP software according to EU-GMP standards.
In the process of deploying and maintaining ERP software in the pharmaceutical sector, a range of challenges regarding compliance and quality assurance have raised many questions for businesses. Particularly, validating ERP software according to EU-GMP standards is a crucial part of this process. Below are common questions about the validation of ERP software according to EU-GMP standards that businesses often encounter:
The European Union's Good Manufacturing Practice is a significant set of rules in the pharmaceutical industry, focusing on ensuring safety, quality, and compliance in production. In Annex 11, EU-GMP emphasizes the validation of computerized systems, including both software and hardware, as a crucial factor for the manufacturing process and quality management. This means that every software system and application used in production, supply chain management, and quality control must comply with the strict requirements of Annex 11.
With this comprehensive definition, businesses need to ensure not only the functionality and utility of the software but also the data integrity of the ERP system. The validation of ERP software focuses not only on the deployment phase but also on maintenance, upkeep, and system updates over time.
ERP software needs to adhere to the principles of Data Integrity (ALCOA) issued by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and also referenced in EU-GMP guidelines. Data Integrity ensures that data is Attributable, Legible, Contemporaneous, Original, and Accurate. This linkage is crucial to maintaining the reliability of data generated and processed in the ERP system. The Data Integrity principles are referenced in EU-GMP regulations in Chapter 4 (Part I): Documentation; Chapter 6 (Part I): Quality Control; Chapter 5 (Part II): Processing Equipment (computer systems); Chapter 6 (Part II): Documentation and Records.
The time required for ERP software validation depends on the complexity of the system, project scale, and specific business requirements. Therefore, there is no specific timeframe for ERP software validation. The crucial aspect is to ensure that the validation process is conducted carefully to ensure the integrity and performance of the ERP system over an extended period.
The timeframe for revalidating ERP software depends on various factors, including business developments and changes, as well as software updates. Periodic review of revalidation, as well as after significant updates, ensures that the ERP system continues to meet new regulations and maintains high performance.
In the context of the pharmaceutical industry imposing increasingly high demands on quality and compliance standards, the use of modern solutions like ERP PharmaSoft has become a decisive factor in ensuring compliance with EU-GMP standards. With immensely significant benefits, ERP PharmaSoft is a powerful management tool for pharmaceutical businesses to enhance production efficiency and comply with the strict requirements of GMP standards. The benefits of using ERP PharmaSoft for EU-GMP compliance include:
1. Compliance with EU-GMP Quality Standards: ERP PharmaSoft is designed specifically for GMP compliance in the pharmaceutical sector. The software provides solutions aligned with EU-GMP standards, ensuring that the ERP system meets the specific requirements of pharmaceutical manufacturing and distribution.
2. Continuous Updates and Compliance Monitoring: ERP PharmaSoft offers continuous updates and compliance monitoring. This is crucial in the context of regularly changing regulations, where maintaining GMP standards is essential. Regular updates help address new challenges and ensure ongoing compliance with evolving regulations.
3. Efficient Troubleshooting and Issue Resolution: In the case of problems or deviations, ERP PharmaSoft's technical specialists provide timely and effective troubleshooting solutions. This minimizes downtime and ensures the smooth and reliable operation of the ERP system, contributing to overall efficiency in pharmaceutical production processes.
Therefore, validating ERP software according to EU-GMP standards is an essential factor in ensuring the accuracy, integrity, and security of data in the pharmaceutical industry. The use of ERP PharmaSoft enhances these efforts by providing suitable solutions, continuous updates, and effective issue resolution, ultimately contributing to the seamless operation of the ERP system within the framework of GMP compliance.
To learn more about the ERP PharmaSoft software system and its features designed to comply with EU-GMP regulations, please contact:
EnterSoft Software Solutions Joint Stock Company
Email: info@entersoft.com.vn - kinhdoanh@entersoft.com.vn
Phone: 0985.200.060
Website: www.entersoft.com.vn
Reference:
1. Annex 11: Computerised Systems, Good Manufacturing Practice Medicinal Products for Human and Veterinary Use, European Medicines Agency (EMA)
2. Guidance on good manufacturing practice and good distribution practice: Questions and answers, European Medicines Agency (EMA)
3. Data Integrity and Compliance With Drug CGMP Questions and Answers Guidance for Industry, Food And Drug Administration (FDA)
ERP stands for Enterprise Resource Planning, loosely translated as Enterprise Resource Planning System. That's the linguistic interpretation, so what is the true essence of ERP?
In essence, ERP is an integrated software system that combines all of the core business processes and necessary data to operate and manage a company. The ERP-PharmaSoft software brings efficiency in managing businesses, especially for companies in the pharmaceutical industry.
This article provides a detailed guide on the steps to implement an ERP system for pharmaceutical businesses and highlights the key considerations to keep in mind during implementation.
With double-digit growth potential, the pharmaceutical industry in Vietnam is a lucrative market for businesses. To capitalize on this opportunity, companies have overcome management limitations by using modern ERP systems.
With the development of information technology in the pharmaceutical industry, PharmaSoft has become a trusted partner in driving digital transformation for pharmaceutical businesses.
The article introduces the benefits and ways to use the ERP PharmaSoft software in sales management and optimizing business processes for businesses.
With the growth and development of the product distribution field, EnterSoft has developed EnterDMS - a distribution channel management software.
Pharmasoft provides advanced features for monitoring and managing the quality of pharmaceuticals, including document management, product profiles, and manufacturing processes.
Using ERP software to optimize warehouse management processes is an intelligent solution that many businesses are adopting, and ERP PharmaSoft is one of them.
If you are involved in the goods distribution industry, you will certainly be interested in DMS software - a modern technological solution that helps efficiently and professionally manage and operate distribution channel systems.
One of the important features of PharmaSoft is the ability to create electronic batch records for each pharmaceutical batch. In this article, we will introduce the electronic batch record function in the PharmaSoft ERP software.
In this article, we will focus on ERP software for the manufacturing industry, which is one of the sectors with high demand for managing and operating complex and diverse processes.
Have you ever wondered why GMP-compliant businesses trust and choose PharmaSoft as their comprehensive management tool? Let's explore the secrets of success that PharmaSoft brings to enterprises and the reasons why there are few better options.
After 20 years of operation in the field of developing software for managing veterinary medicine production, EnterSoft has conducted research and analysis on some challenges and underlying causes behind the current state of the veterinary medicine industry. Furthermore, they have proposed solutions for improvement.
In this article, let's explore the Human Resources and Payroll Management module in ERP-PharmaSoft, a comprehensive solution for businesses operating in the manufacturing field.
With its advanced purchasing management module, businesses can enhance efficiency and optimize the purchasing process. Utilizing this module helps automate steps from creating purchase requests, evaluating suppliers, and placing orders, to inventory receipt and payment.
But have you ever wondered, "How can we effectively build and manage GMP processes?" This article will provide you with an overview of GMP standards and detailed guidance on integrating GMP processes into an Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system.
This article will introduce the concept, features, and benefits of DMS software, as well as guide you on how to choose and implement this software for your business. How Distribution Management System (DMS) Software Helps Businesses Increase Sales and Efficiency
In this article, we will discuss some common difficulties encountered in managing businesses engaged in packaging production and distribution. Additionally, we will propose some feasible management solutions to overcome these challenges and enhance overall business efficiency.
Intelligent reporting not only provides information about the current state of the business but also offers forecasts, recommendations, and necessary actions to improve business outcomes.
To design an effective e-commerce website, you need to follow a specific process and prepare diligently. In this article, EnterSoft will introduce you to the step-by-step process of designing an e-commerce website from A to Z.
EnterSoft will share some tips for implementing EnterERP management software in the manufacturing industry, from preparation and design to operation and maintenance. We hope this article will provide useful and practical information for businesses.
To address these challenges, businesses need a comprehensive, integrated, and intelligent management solution. EnterERP is precisely that – an Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system designed specifically for manufacturing and distribution enterprises.
The goal of this article is to present the important factors that pharmaceutical companies need to consider when selecting management software.
To Succeed in Implementing ERP in the Pharmaceutical Industry, Businesses Need to Master Key Factors and Adhere to Fundamental Principles.
EnterSoft will present the significant concerns that businesses in the pharmaceutical field commonly encounter when facing the process of selecting ERP software.
PharmaSoft, short for "Pharmaceutical Software," is a comprehensive enterprise management software specially developed for the pharmaceutical industry, following the Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) model.
To address the challenges and leverage opportunities, pharmaceutical manufacturing companies need to implement new technology management solutions.
ERP is a comprehensive enterprise management solution that helps businesses integrate all operational processes into a single system. Applying ERP in factories and manufacturing enterprises brings many significant benefits, enhancing management efficiency, increasing competitiveness, and meeting market requirements.
A Custom ERP Software (Enterprise Resource Planning) system is a business management solution specially designed to meet the specific needs and workflows of an organization.
While many pre-packaged ERP solutions are available, the demand for custom-designed ERP software still exists in large-scale enterprises with unique characteristics and specific requirements.
There are three main types of ERP systems: Cloud ERP, On-Premises ERP, and Hybrid ERP. Each type has its advantages and disadvantages, making them suitable for different types of businesses.
In this article, EnterSoft will introduce you to the initial steps to begin with ERP software.
Managing and ensuring product quality is a vital factor in the pharmaceutical, cosmetics, food, medical equipment industries, etc. The Quality Assurance (QA) department not only complies with regulations but also manages the entire product lifecycle from raw materials to handling returns. This requires a high degree of accuracy, consistency, and transparency. So how does the QA department effectively manage this enormous workload?