6 signs that help leaders not miss business improvement opportunities
The signs indicating the need for business improvement are warnings about potential or existing issues that the business is facing.
In today's business world, the term "Business Intelligence" is not just a concept, but a decisive strategy for the success or failure of a business. This article will delve deeper into Business Intelligence and how using data and intelligent analysis determines success and failure in a competitive environment.
Business Intelligence (BI) is the process of collecting, analyzing, and utilizing data to support decision-making within a business. Business Intelligence assists business managers in decision-making by providing accurate and timely information.
The main idea of Business Intelligence is that if managers have accurate or complete information, they are prone to making ineffective decisions, such as purchasing items at the wrong time or investing in unprofitable projects. The concept of "Garbage In Garbage Out - GIGO" describes this well: if the input data is not good, the analysis results will not be reliable. Business Intelligence tries to address this issue by analyzing current data and presenting it understandably through dashboards with specific figures.
Business Intelligence must ensure accuracy, timeliness, and sufficient data volume. This means collecting enough information, checking to ensure data integrity, and structuring data for easy analysis. For example, a manufacturing plant needs to accurately record the number of defective products each day to improve the production process.
In reality, many companies have unstructured data or data in different formats, making data collection and analysis difficult. Software solution companies have provided Business Intelligence solutions to optimize the collection and analysis of this data. These solutions are often enterprise software applications that unify and analyze data from various sources. For example, an intelligent Business system can collect data from different retail stores and analyze it to identify customer buying trends.
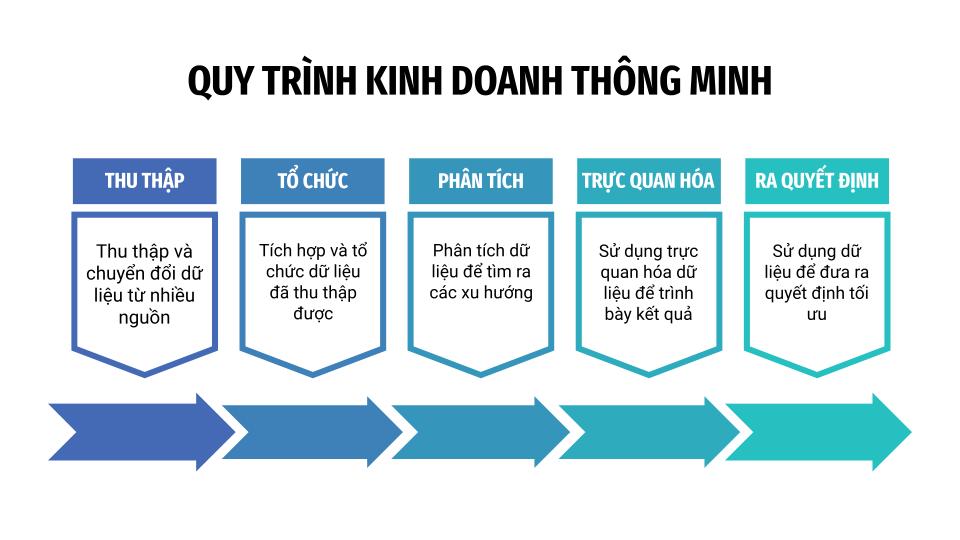
Step 1: Collecting and converting data from multiple sources
First, Business Intelligence begins by gathering data from various sources such as Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems, Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems, websites, social media, and direct sales channels.
Data collected from these sources often come in various formats. Business Intelligence utilizes data transformation tools to consolidate and standardize information, turning raw data into a usable format for analysis. For example, sales data from physical and online stores can be merged to create an overall picture of revenue.
Step 2: Integrating and organizing collected data
After data is collected and transformed, the next step is to integrate and organize the data. Data from different sources is placed into a data warehouse or centralized data management system. The data is then sorted and classified according to criteria such as customers, products, time, geographical area, facilitating easy retrieval and analysis. For example, a retail company may organize sales data by quarters in a year to track and compare revenue.
Step 3: Data analysis
Once the data has been integrated and organized, the next step is data analysis to uncover trends and valuable insights. Business Intelligence data analysis tools help identify patterns and trends, thereby providing valuable information. Data analysis is categorized into 4 main types:
• Descriptive analytics provide reports and summaries of data.
• Diagnostic analytics identify the causes of phenomena and trends.
• Predictive analytics use statistical models and machine learning to forecast future trends.
• Prescriptive analytics provide recommendations for optimal actions.
For example, a retailer may analyze data to identify best-selling products and peak times, aiding in adjusting marketing strategies. An insurance company may predict customer risks to adjust insurance premiums. This process helps businesses optimize operations and make strategic decisions based on data.
Step 4: Utilize data visualization to present results
Data visualization is an integral part of Business Intelligence, helping to present analysis results understandably and visually. Instead of relying solely on dry numerical tables, Business Intelligence uses charts, graphs, and interactive dashboards to illustrate analysis results. For example, a company may use line charts to track monthly revenue or bar charts to compare sales figures between products. Data visualization helps managers quickly grasp information and make data-driven decisions.
Step 5: Utilize data to make optimal decisions
The strength of Business Intelligence lies in its ability to provide deep and detailed information in real-time, allowing businesses to take immediate action based on what they see. For example, if a retailer discovers that a product is selling rapidly, they can quickly adjust inventory to ensure no shortages occur. Another example is in manufacturing, where if Business Intelligence data indicates a decrease in the performance of a machine, the business can immediately proceed with maintenance to avoid production interruptions.
• Increased operational efficiency: Business Intelligence helps automate many processes, from data collection to analysis and reporting. Manufacturers can utilize Business Intelligence to optimize production processes, minimize waste, and increase productivity.
• Deep understanding of customer behavior and shopping habits: Business Intelligence provides detailed insights into customer behavior, helping businesses better understand their needs and preferences. For instance, an online retailer can use Business Intelligence to analyze patterns of products sold and adjust marketing strategies accordingly.
• Accurate performance evaluation: Business Intelligence reports provide detailed and accurate information about the performance of various departments within the business. For example, a company can track the performance of marketing campaigns to identify which campaigns are most effective.
• Comparison of historical and current data: Business Intelligence allows businesses to compare current performance with past data to assess progress and identify areas for improvement. Businesses can compare current quarter profits with previous quarters to evaluate business effectiveness.
• Real-time sharing of analyses between departments: Business Intelligence enables quick and easy sharing of analysis results between departments within the business, enhancing collaboration and making collective decisions. For example, the sales and marketing departments can share information about purchasing trends to adjust strategies accordingly.
• Sales and Marketing: Business Intelligence provides data on purchase history, customer feedback, and market trends, optimizing the sales and marketing process from product pricing to advertising and promotion.
• Corporate Finance: Imagine being able to automatically record and analyze every expense from raw materials to shipping. Business Intelligence provides an overview of the company's financial situation, from monitoring operating costs to managing financial resources, optimizing costs, and significantly enhancing profits.
• Improving Supply Chain Efficiency: Managing the supply chain is crucial to ensuring that all goods are delivered on time and to the right place. Business Intelligence optimizes this process by providing accurate and timely information, from ordering to shipping.
• Improving Data Accuracy: Accurate data is crucial for effective and reliable decision-making. Business Intelligence optimizes the data collection and processing process, from automating recording to using advanced data analysis tools, minimizing reliance on inaccurate data and providing a reliable foundation for strategic decisions.
• Faster, More Accurate Decision-Making: Using Business Intelligence is like having a dashboard that synthesizes all crucial information about business activities. This helps managers make faster and more accurate decisions, from production planning to human resource management and other resources.
• Enhancing Transparency: Transparency is one of the most important factors in building trust from customers and partners. Business Intelligence provides monitoring and reporting tools, from tracking production activities to managing operational processes. This helps create a transparent working environment, where all activities are public and controlled, thereby enhancing trust and satisfaction from customers and partners.
• Security and Compliance: Compliance with security and transparency regulations is extremely important. Business Intelligence provides monitoring and reporting tools to ensure that all activities comply with regulations, from data management to system security.
• Skill Shortage: There is a significant shortage of data handling skills. This can pose many difficulties in understanding and using information correctly. For individuals and businesses, the ability to analyze and leverage data is a decisive factor in success. Therefore, training and developing these skills become extremely important to meet the increasing demand for information and data.
• Upfront Costs: While developing a robust Business Intelligence system may require relatively large costs, the long-term benefits can offset the initial investment. Intelligent analysis helps optimize costs and enhance profits, helping businesses save more than upfront costs.
• Organizational Culture Change: Finally, an equally important challenge is the change in organizational culture to adapt to the Business Intelligence environment. This includes promoting the acceptance and use of new technologies, changing work processes, creating an open, flexible and innovation-ready work environment.
>>> Related: Building Skills for Employees to Adapt to Digital Transformation
Data is the lifeblood of successful organizations. Decision-makers can use this knowledge to improve decision-making and productivity across the entire enterprise. Organizations benefit when they can assess all activities and processes, understand customers, evaluate the market, and drive improvements. They need appropriate tools to aggregate business information from everywhere, analyze, explore data-based information, and find solutions. To provide an effective Business Intelligence system that meets management needs well, organizations should:
• Set Clear Business Goals: Identify the most valuable and useful information to help the organization know what data to collect and from where. This also helps in selecting the necessary features to provide that information.
• User Training: Changing the culture to become a data-driven organization is most effective when all users are clearly and engagingly trained on new tools. Superficial training or self-learning may not encourage team engagement and may yield inaccurate results.
• Monitor Data Quality: Continuous monitoring of data is necessary to ensure consistent and reliable results. As market conditions change, additional measures or the development of different reporting formats may be necessary to enhance clarity. Input datasets must be rational, unbiased, and managed according to clear governance standards to ensure safe, private, accurate, and usable data.
• Ensure Data Access for Decision-Makers: To make accurate and timely decisions, decision-makers need easy access to critical data. This can be achieved by setting up user-friendly BI systems and providing role-based access to protect sensitive data.
A real-life example is a pharmaceutical company using the ERP system PharmaSoft to manage manufacturing, distribution, and finance. This system helps the company track the entire manufacturing process from raw materials to finished products, ensuring quality and efficiency. By using Business Intelligence tools, the company can analyze data from manufacturing processes, forecast market demand, and adjust production plans accordingly. This not only helps optimize the manufacturing process but also improves customer service and enhances competitiveness in the market.
In conclusion, Business Intelligence is not just a technological tool but also a comprehensive strategy that helps businesses improve efficiency, understand customers and markets better, and make strategic decisions based on data. For business managers, implementing Business Intelligence is a crucial step towards achieving success and sustainable development.
>>> Related: Benefits of Data-Driven Business Management
To learn more about the ERP PharmaSoft software system and its features designed to comply with EU-GMP regulations, please contact:
EnterSoft Software Solutions Joint Stock Company
Email: info@entersoft.com.vn - kinhdoanh@entersoft.com.vn
Phone: 0985.200.060
Website: www.entersoft.com.vn
The signs indicating the need for business improvement are warnings about potential or existing issues that the business is facing.
Let's embark on a promising journey as the encounter between digital transformation and production management has opened new doors.
The role of employees in digital transformation is not just about using technology, but also about changing mindsets and approaching work. Employees need to have the ability to understand and use digital tools while also applying critical thinking and creativity to leverage opportunities and address new challenges.
Digital transformation is not only about using digital tools, but also about changing the culture, mindset, and ways of working within the organization. In this article, we will introduce some real-life examples of successful digital transformation in Vietnam and around the world, so that you can learn from them and apply them to your own work.
Digital transformation has become an essential requirement in the modern business world. Digital transformation enhances the productivity, efficiency, creativity, and competitiveness of businesses.
Effective leadership can drive and guide the transformation process, ensuring that the organization adapts to the digital age and thrives in the digital economy. This article explores the significant role of leaders in promoting and managing digital transformation initiatives.
In today's digital age, there are several commonly used concepts related to digital transformation, but not everyone understands their meanings and differences clearly. In this article, we will explain and differentiate three important concepts in digital transformation: information digitization, process digitization, and digital transformation.
In this article, EnterSoft will introduce some of the new management trends in the manufacturing industry and how to apply them in practice.
Data-driven business management is no longer a novel concept; it has become an essential trend that brings numerous important and diverse benefits. Below, we will go through some examples of the actual benefits that data-driven business management has brought.
This article will delve into understanding the challenges that Vietnamese businesses are currently encountering in supply chain management, along with intelligent management strategies to overcome these challenges.
Let's delve into the concept and benefits of the lean production method, along with the methods and steps involved in its implementation.
The manufacturing sector has undergone significant transformation in the modern era, particularly with the robust development of information technology. Digital transformation in manufacturing is becoming an important and inevitable trend. This article aims to explore the significance of digital transformation in the manufacturing sector, uncover the potential and benefits of this process, and also consider the challenges and risks that may arise.
To safeguard data integrity, organizations and individuals must apply principles, methods, and tools suitable for their purpose, scale, and industry. This article will introduce the concept, principles, and data integrity methods in the pharmaceutical manufacturing field.